

Workstation Name : machine name from which logon attempt was performed.
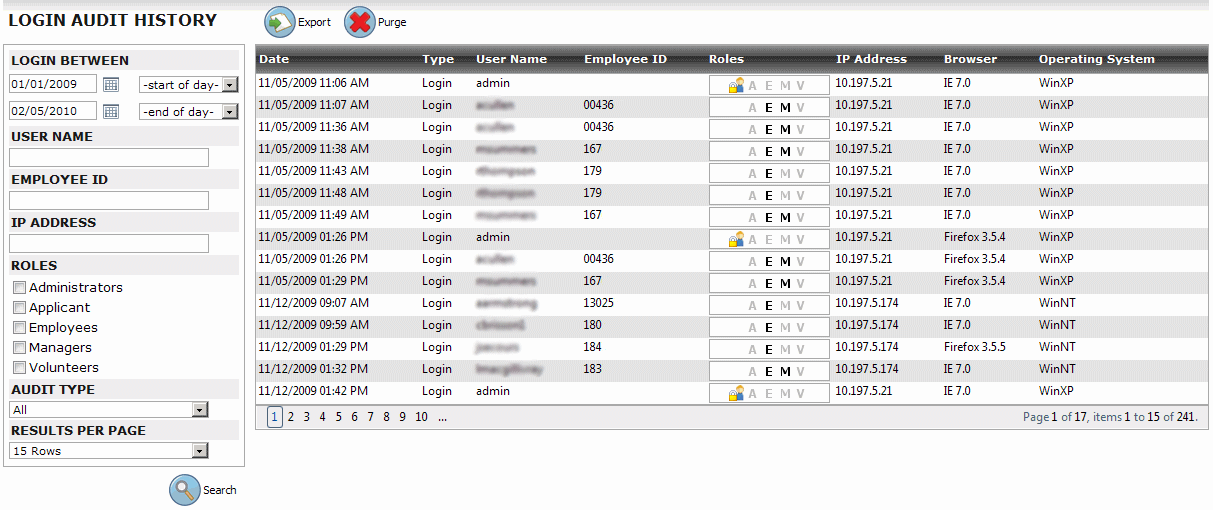
#Login audit full#
You can also correlate this process ID with a process ID in other events, for example, " 4688: A new process has been created" Process Information\New Process ID.Ĭaller Process Name : full path and the name of the executable for the process. If you convert the hexadecimal value to decimal, you can compare it to the values in Task Manager. To see the PID for a specific process you can, for example, use Task Manager (Details tab, PID column): Process ID (PID) is a number used by the operating system to uniquely identify an active process. Sub Status : additional information about logon failure.įor more information about various Status or Sub Status codes, see NTSTATUS Values.Ĭaller Process ID : hexadecimal Process ID of the process that attempted the logon. For this event, it typically has " 0xC0000234" value. For this event, it typically has " Account locked out" value.
Logon ID : hexadecimal value that can help you correlate this event with recent events that might contain the same Logon ID, for example, " 4624: An account was successfully logged on."įailure Reason : textual explanation of Status field value. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.Īccount Name : the name of the account that was specified in the logon attempt.Īccount Domain : domain or computer name. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. Security ID : SID of the account that was specified in the logon attempt.

The domain controller was not contacted to verify the credentials. The new logon session has the same local identity, but uses different credentials for other network connections.Ī user logged on to this computer remotely using Terminal Services or Remote Desktop.Ī user logged on to this computer with network credentials that were stored locally on the computer. The credentials do not traverse the network in plaintext (also called cleartext).Ī caller cloned its current token and specified new credentials for outbound connections. The built-in authentication packages all hash credentials before sending them across the network.
#Login audit password#
The user's password was passed to the authentication package in its unhashed form.
#Login audit windows#
Windows Logon Types" contains the list of possible values for this field.Ī user or computer logged on to this computer from the network.īatch logon type is used by batch servers, where processes may be executing on behalf of a user without their direct intervention.Ī service was started by the Service Control Manager.Ī user logged on to this computer from the network. Logon Type : the type of logon that was performed. Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCALįor some well-known security principals, such as LOCAL SERVICE or ANONYMOUS LOGON, the value of this field is "NT AUTHORITY".įor local user accounts, this field will contain the name of the computer or device that this account belongs to, for example: "Win81". Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers.Īccount Name : the name of the account that reported information about logon failure.Īccount Domain : subject's domain or computer name.

When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.Ī security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Security ID : SID of account that reported information about logon failure. Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista. For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
